LDAP-based Authentication for SwiftStackAuth¶
This middleware is designed to allow a company's LDAP authentication information to verify the Swift X-Auth-User and X-Auth-Key fields as a user logs in.
To get to the configuration page, sign into your SwiftStack Controller account, click on the Clusters tab and then click Manage for the cluster. Click the Middleware tab. Under the Available Swift Middleware section, locate and click on the LDAP-based Authentication for SwiftStackAuth row.
Settings¶
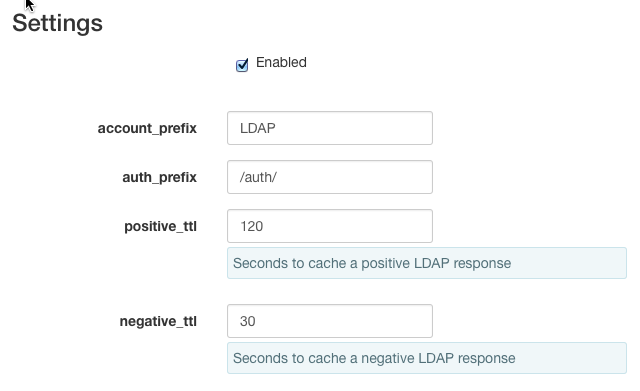
Be sure the Enabled box is checked if you want the settings you provide on the page to be used to authenticate users.
All fields above the individual LDAP server configurations are required.
account_prefix
This field is filled in by default.
auth_prefix
This field is filled in by default.
Note
If more than one type of authentication middleware is being used simultaneously, the account_prefix and the auth_prefix fields may need to be modified. Please consult with SwiftStack Support to determine the correct values needed.
positive_ttl
This time is how long to cache the results of an LDAP lookup. A default time is provided and can be changed to any preferred time (0 or greater).
negative_ttl
This time is how long to cache the results of an LDAP lookup. A default time is provided and can be changed to any preferred time (0 or greater).
Configuration For Each LDAP Server¶
In a small LDAP installation, a single LDAP endpoint might contain the entire directory. However, in a large organization which has only recently merged separate divisions' LDAP installations, it may be necessary to query several independent LDAP endpoints in order to get an authoritative answer. For this reason, SwiftStack's LDAP infrastructure supports multiple independent LDAP server configurations. The discussion below applies to each LDAP endpoint that is configured.
Required Parameters¶
Server URI
The Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) field should contain the ldap uri in the form of ldap://<hostname or IP address> or ldaps://<hostname or IP address>, e.g.ldap://192.0.43.10
Transport
LDAP (unencrypted) or LDAP with StartTLS (encrypted)
Warning
If using secure LDAP (either ldaps or StartTLS), the nodes must be configured to accept the LDAP server's certificate. This is not configured by the SwiftStack controller.
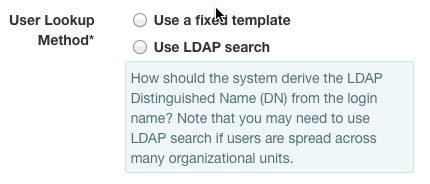
User Lookup Method¶
In addition to the Server URI and Transport parameters, also
required is a way to map usernames to LDAP Distinguished Names.
Tip
Different LDAP installations will be configured with different directory structures, so please be sure to verify the field names and types that your LDAP server supports, in order to correctly configure the LDAP support.
One of two relationships must be used.
LDAP uniquely identifies its entries by Distinguished Name (DN), but users
rarely log in with the full DN. If the user's X-Auth-User (username or
login identifier) can be interpolated into a fixed template (such as
cn={username},ou=people,dc=example,dc=com), then LDAP support can be
configured to Use a fixed template.
If the user's X-Auth-User is not part of the DN but is the value of an
attribute, then Use LDAP search must be defined.
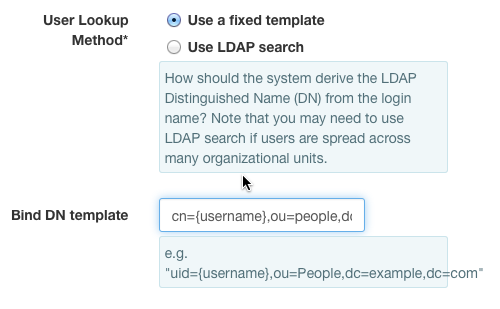
Use A Fixed Template¶
Single variable¶
X-Auth-User provided by the user is represented by the variable
{username} in the LDAP settings.
Consider a directory with this structure:
1 2 3 4 5 | dn: cn=John Doe,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: pilotPerson
cn: John Doe
sn: Doe
userPassword: changeme
|
If John Doe logs in using "John Doe" (which matches the cn) for
the X-Auth-User, then:
Select Use A Fixed TemplateSetBind DN templateto cn={username},ou=people,dc=example,dc=com.
Multi-Variable¶
If your LDAP server requires the user to provide multiple pieces of information to identify themselves then a multi-variable template or user search can be configured. For this example the LDAP server will require the user's UID, the customer's OU, and the franchise's OU. The LDAP record for a user called "1 A alpha" would look like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | dn: uid=test_customer1a_alpha,ou=Customer1A,ou=Franchise1,dc=example,dc=com
uid: test_customer1a_alpha
cn: 1 A alpha
uidNumber: 2001
gidNumber: 10000
homeDirectory: /home/1Aa
role:
objectclass: account
objectclass: simpleSecurityObject
objectclass: extensibleObject
objectClass: posixAccount
|
In this case, the user would provide a composite username for authentication separating each required part by a colon, e.g. Franchise1:Customer1A:test_customer1a_alpha.
The user input is read in order and each part numbered starting with zero. e.g. Franchise1 = 0, Customer1A = 1. These numbered variables are then used for the verification.
Select Use A Fixed TemplateSetBind DN templateto uid={2},ou={1},ou={0},dc=example,dc=com.
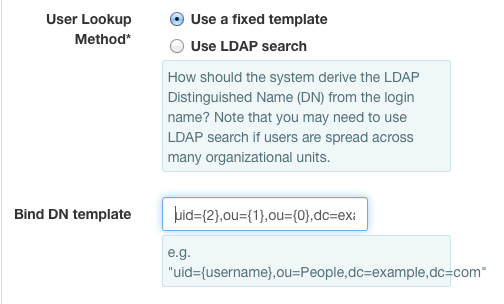
The numbered variables may also be used in the User search DN and
User search template fields as necessary.
Use LDAP search¶
This option is appropriate if your directory has a structure such as the following:
ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
dn=employeeId=1234,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
uid=alice
givenName=Alice
surname=Smith
homeDir=/users/alice
...
dn=employeeId=5678,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
uid=bob
givenName=Robert
surname=Jones
homeDir=/users/bob
...
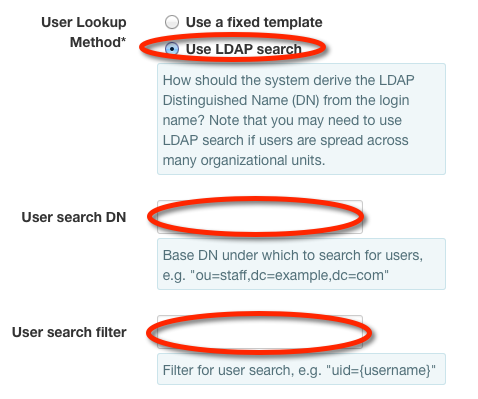
If user Alice Smith logs in with "alice" for the X-Auth-User, it cannot be found directly in the DN, so we must configure a search. For this example:
SetUser search DNfield to ou=people,dc=example,dc=com.SetUser search templatefield to uid={username}.
Restrictions On Users¶
It may be the case that some valid LDAP users should not be allowed to authenticate. You may choose to configure access by group, whitelist restrictions (only the specified users are allowed) or blacklist restrictions (only the specified users are disallowed). You may even configure all three types, in which case the user must pass all restrictions.

Use LDAP group membership¶
Only LDAP users who are a member of the defined group may authenticate.
This option is appropriate if your directory maintains permissions in a structure such as the following:
ou=products,dc=example,dc=com
ou=swift_product,ou=products,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: groupOfNames
member: uid=alice,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
member: uid=bob,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
member: ...
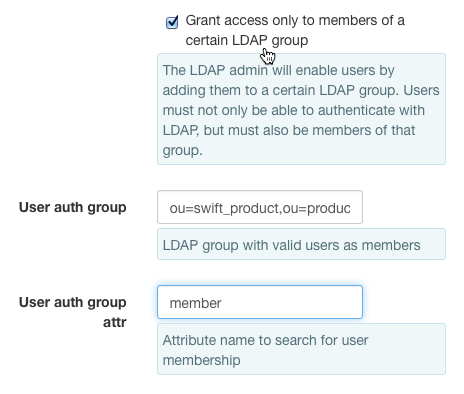
- For this example:
- Set the
User auth groupfield to ou=swift_product,ou=products,dc=example,dc=comSet theUser auth group attrfield to member
Note that the structure of an LDAP posixGroup is slightly different from
a groupOfNames:
cn=admins,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: posixGroup
memberUid: alice
memberUid: bob
memberUid: ...
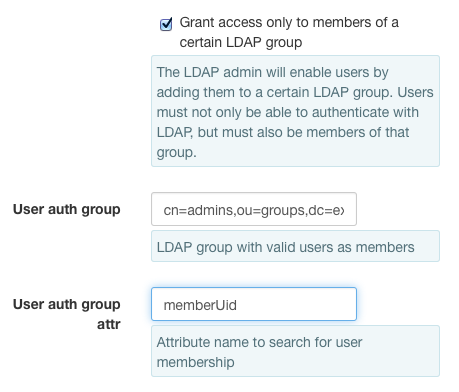
- For this example:
- Set the
User auth groupfield to cn=admins,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=comSet theUser auth group attrfield to memberUid
Whitelist and Blacklist¶
Whitelist and Blacklist restrictions may be any valid LDAP filter string, which gives great flexibility. For information on LDAP search filters, many guides are available online (e.g. the guides provided by CentOS and Microsoft). For a formal reference on LDAP search filters, see the appropriate section of RFC 4511 .
To configure a restriction filter on LDAP users, select the appropriate checkbox and fill in the filter value:
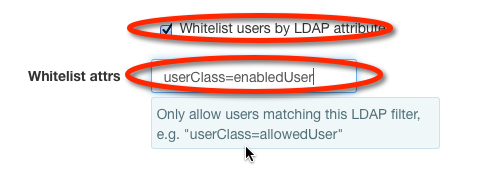
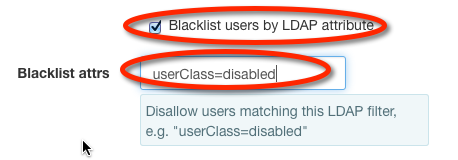
Note
The example filter userClass=swiftUser depends upon cosine.schema (RFC 1274) being installed and the objectClass for the user being pilotPerson. Adding arbitrary key:value pairs not defined in the object type's schema to user definitions may cause the user to fail authentication.
Select your Swift account authorization model¶
Selecting Use LDAP groups will allow an authenticated user access to both Swift accounts named for the groups they are a member of, as well as the account whose name matches their LDAP login name.
Define Your LDAP Group Structure¶
Authorization by LDAP Group is required for Controller LDAP, but optional for LDAP Auth Middleware.

There are multiple ways to configure groups under LDAP. In the event yours is not described here, please contact Technical Support for assistance.
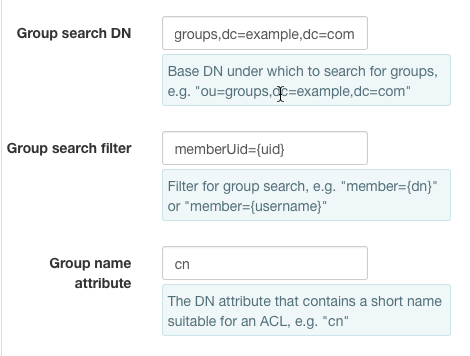
posixGroups¶
LDAP's posixGroup entries list the shortened names of their members. If your groups belong to objectClass posixGroup and look something like
1 2 3 4 5 | dn: cn=swiftPosix,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: posixGroup
cn: swiftPosix
gidNumber: 10001
memberUid: some
|
- Then set
Group search DNto ou=groups,dc=example,dc=comGroup search templateto memberUid={uid}Group name attributeto cn
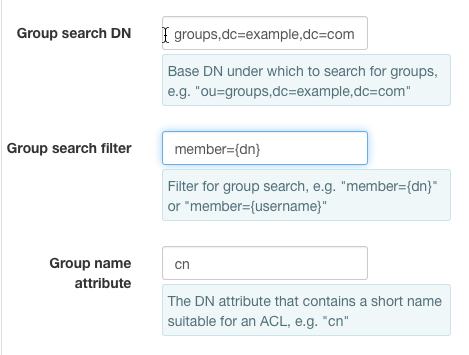
groupOfNames¶
LDAP's groupOfNames entries list the complete DNs of their members. If your group belongs to objectClass groupOfNames and looks something like
1 2 3 4 | dn: cn=swift,ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com
objectClass: groupOfNames
cn: swift
member: cn=John White,ou=people,dc=example,dc=com
|
- Then set
Group search DNto ou=groups,dc=example,dc=comGroup search templateto member={dn}Group name attributeto cn
Configure LDAP Search¶
The process of authenticating and authorizing an LDAP user is likely to require the system to perform LDAP queries beyond simple LDAP bind (password verification) operations. These LDAP queries include:
- If Use A Fixed Template is not configured, then looking up a user requires searching the directory for an attribute-value pair.
- If Whitelist/Blacklist Filters are configured, then the system must retrieve the user's attributes to check if the user should be filtered.
- If Grant access only to members of a certain LDAP group is selected, the system must look up that group's membership.
- If Use LDAP groups for authorization is selected, then the system must query all groups to find the ones containing the user as a member.
Because of this, the system needs a way to perform read-only searches of the LDAP directory.
Some LDAP directories are configured to allow anonymous clients to perform searches. If this is your situation, select Anonymous LDAP Search for your LDAP search method.
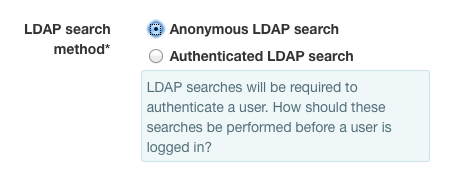
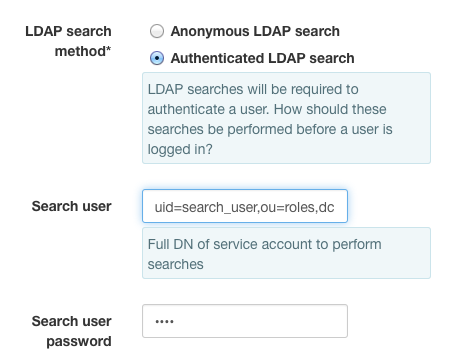
However, for security reasons, it is common for LDAP administrators to prohibit
anonymous searches. In this case, you will need to use a role account to
perform the search. If your LDAP search role account has the DC
uid=search_user,ou=roles,dc=example,dc=com, then you would select
Authenticated LDAP Search and configure the fields like this:
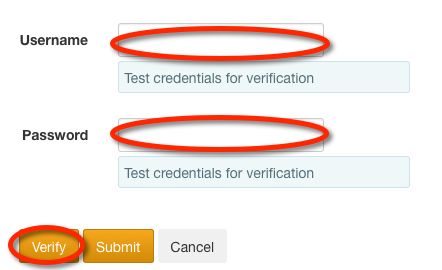
Verify Settings¶
Once you have filled in the user and/or groups settings you can verify your
middleware configuration in the Verify Settings section. Provide the
Search user and Search user password for an account on the LDAP server and click
on the Verify button.
The results will return a message about the user being found or not found.
Submit¶
Once you are satisfied with the configuration, click the Submit button to save it.
Note
Remember to Deploy Middleware Changes to apply any changes.
Command Line: Using python-swiftclient with LDAP¶
When you provide your X-Auth-User and X-Auth-Key to the swift
command-line utility or the python-swiftclient library, it returns
a storage url and the auth token. This auth token works with any account
the user has access to, but the storage url will only access the user's
account, not any account they may have access to via group membership. To
access a group's account, replace LDAP_<username> with LDAP_<group name>
in the storage url.
swift Example¶
$ swift stat -v -A http://192.168.22.42/auth/v1.0 -U some -K password
StorageURL: http://192.168.22.42/v1/LDAP_some
Auth Token: AUTH_tkfd3b7b695a4f4de1a8c287898a4b4465
Account: LDAP_some
Containers: 0
Objects: 0
Bytes: 0
Meta Temp-Url-Key: ed94262e-0e66-4333-9f9e-809f2acf8574
X-Timestamp: 1371503771.31799
X-Trans-Id: tx7aa7b4f4c1dc4918aab6e95e163b8901
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
Accept-Ranges: bytes
$ swift post --os-storage-url http://192.168.22.42/v1/LDAP_B --os-auth-token AUTH_tkfd3b7b695a4f4de1a8c287898a4b4465 containerA
$ swift list --os-storage-url http://192.168.22.42/v1/LDAP_B --os-auth-token AUTH_tkfd3b7b695a4f4de1a8c287898a4b4465
containerA
swiftclient Example¶
from swiftclient import get_auth_1_0, head_account
import re
auth_url = "<auth_url>"
username = "<username>"
password = "<password>"
group_name = "<group name>"
url, token = get_auth_1_0(auth_url, username, password, False)
url = re.sub(username, group_name, url)
head_account(url, token)
Disambiguating Multiple LDAP Endpoints¶
Since it is possible to define multiple LDAP endpoints in the middleware, it is
sometimes necessary to be able to specify which endpoint to search at when
authenticating. In order to do this, there is a special header named
X-Auth-Domain which will allow you to specify. Unfortunately, the swift
utility does not allow you to specify this header, so authenticating this way
requires making HTTP requests manually, for example via cURL:
curl -H 'X-Auth-User: username' -H 'X-Auth-Key: password' -H 'X-Auth-Domain: ldap://ldap.example.com/' -D- https://swift.example.com/auth/v1.0
The value of the X-Auth-Domain header must be the same as one of the servers you have configured. If a different server name is provided, a 400 Bad Request will be returned. Otherwise, only the provided server will be searched with the given credentials.